# 10 Hybrid Work Best Practices for Effective Meetings in 2025
Hybrid work is more than a mix of in-office and remote days. It's a different way to operate. The friction points are obvious: choppy video calls, confusion over availability, and the feeling that remote team members are missing key conversations. Transplanting old office habits into a distributed environment doesn’t work. The difference between a high-functioning hybrid team and a frustrated one comes down to a set of intentional, practical rules.
This guide lists actionable hybrid work best practices to address these common problems. We will skip the vague advice and focus on the technical and procedural specifics that create a seamless experience. You will find concrete steps for standardizing meeting controls, establishing clear communication etiquette, and designing schedules that protect focus time. The goal is to build a system that feels fair and efficient for everyone, regardless of their physical location.
To implement these practices, you first need to understand the different ways organizations can structure their approach. Each of the various hybrid work models (opens new window) has its own operational demands. Choosing a model clarifies which of the following best practices will be most important for your team. From there, you can build a framework that supports productivity and inclusion, making your hybrid setup a competitive advantage instead of a logistical headache. We will explore ten key areas, from hardware tips to performance management strategies.
# 1. Standardize Meeting Controls Across Platforms
One of the most persistent frustrations of hybrid work is the platform-switching shuffle. Jumping between Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Webex means constantly relearning where the mute, camera, and share screen buttons are. This mental friction adds up over dozens of calls, increasing the risk of "hot mic" moments or fumbling to share a presentation. Standardizing meeting controls removes this cognitive load.
The idea is to create a universal interface for core meeting functions that works the same regardless of the software. This is an effective hybrid work best practice because it builds muscle memory, making meeting interactions faster and less prone to error.
# How to Implement Universal Controls
You can achieve this with software or hardware. Hardware tools like the Elgato Stream Deck let you map commands to physical buttons. A sales professional, for example, could have a dedicated button to launch their slide deck, another to mute their audio, and a third to switch camera views. All of them would work identically whether the client requested a Teams, Zoom, or Google Meet call.
A software-based approach might use tools that create a persistent overlay on your screen or use system-level hotkey managers to unify keyboard shortcuts across applications.
# Actionable Tips for Standardization:
- Assign physical buttons: Use a device like a Stream Deck. Assign one button for mute/unmute, one for camera on/off, and one for screen sharing. Use color-coding for instant recognition, like red for mute and green for camera.
- Create team documentation: Develop a simple one-page guide showing the standard button layout or keyboard shortcuts. Make it part of your onboarding process.
- Test before you present: Run a quick test before an important client call or all-hands meeting to confirm your universal controls are working with the platform being used that day.
# 2. Implement Physical Button Controls for Accessibility
Relying only on a mouse and keyboard shortcuts to manage meetings creates a hidden barrier. Hunting for the mute button or remembering the right hotkey combination splits your focus and can be hard for team members with motor-skill difficulties. Implementing physical, hardware-based controls offers a more intuitive and accessible alternative.
The concept is to assign meeting functions like mute, camera on/off, and screen sharing to dedicated tactile buttons. This is a high-impact hybrid work best practice because it gives immediate haptic and visual feedback, making meeting management effortless and inclusive. It reduces the cognitive strain of navigating software interfaces, letting presenters and participants stay focused on the conversation.
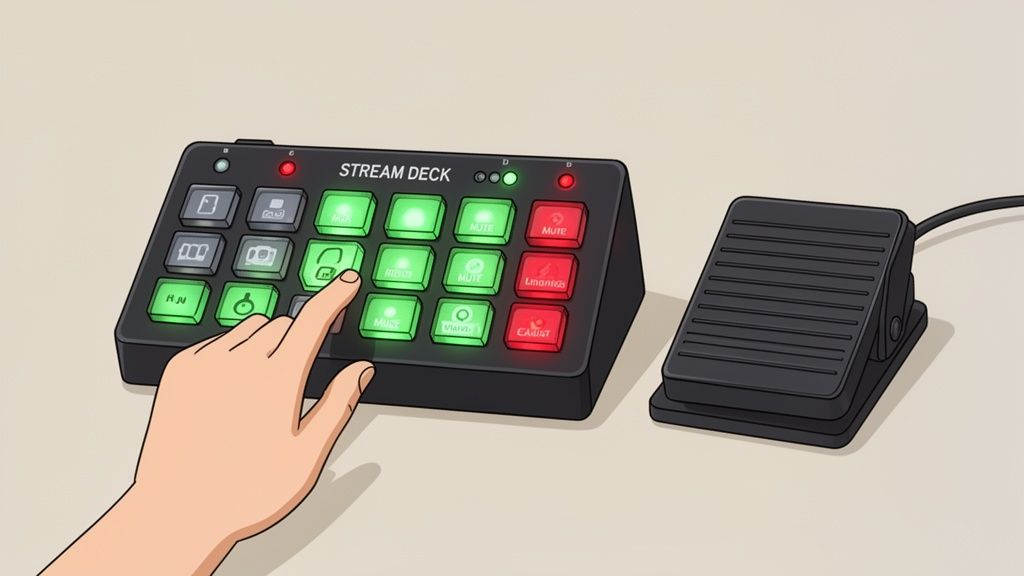

# How to Implement Physical Controls
Hardware like the Elgato Stream Deck or Loupedeck consoles are the most common solution. These devices connect via USB and let you map any keyboard shortcut or complex macro to a single button press. A customer support lead can use a dedicated button to instantly launch their call logging software, mute their mic, and start a screen share with one touch. More specialized tools like foot pedals can be used by professionals, such as translators who need to control recording while keeping their hands free for typing.
Software like MuteDeck can bridge the gap, enabling these hardware devices to work universally across all major video conferencing platforms without needing to be reconfigured for each one.
# Actionable Tips for Physical Controls:
- Start with essentials: Begin by programming 5-7 of your most frequently used controls, such as mute, camera, screen share, leave meeting, and a "raise hand" function.
- Position for ergonomics: Place your control device within easy reach to avoid awkward stretching or wrist strain. Test different positions to find what is most comfortable.
- Consider touchless options: In specialized environments, foot pedals offer a hands-free way to manage functions like push-to-talk or starting/stopping a recording. For an in-depth guide, you can learn more about customizing your Stream Deck from mutedeck.com (opens new window).
# 3. Enable Real-Time Visual Status Indicators
The phrase "you're on mute" is a hallmark of the hybrid work era. A more subtle stressor is the uncertainty: Am I muted? Is my camera on? Glancing away from your audience to hunt for the tiny status icon in a meeting app breaks your flow and feels unprofessional. A persistent, at-a-glance visual indicator solves this by providing immediate confirmation of your microphone, camera, and recording state.
This approach provides a constant, unambiguous feedback loop that sits in your peripheral vision, freeing you from a cycle of double-checking your software interface. This is a simple hybrid work best practice for building confidence and maintaining focus, especially in high-stakes presentations or sensitive conversations where privacy is a concern.
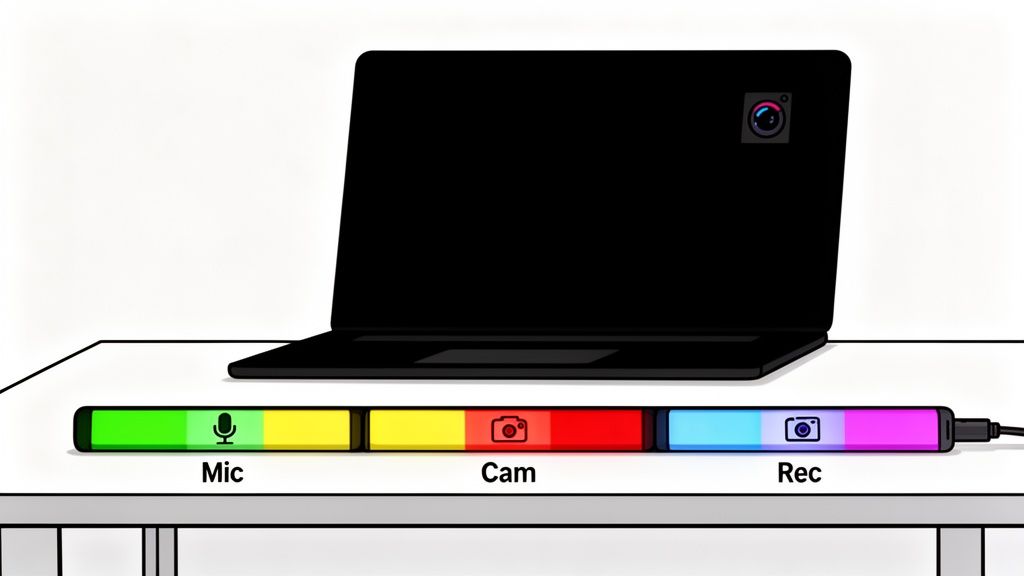
# How to Implement Visual Status Indicators
Both hardware and software can create these always-on status displays. Hardware solutions, often called "on-air" or "busy" lights, are physical LED devices that sit on your desk or monitor. They change color based on your meeting status—a clear signal to both you and any family members or colleagues in your physical space that you're in a live meeting. Online educators, for instance, use these to ensure their microphone is live only when they intend it to be.
Software tools can create a persistent overlay on your screen, like a color bar at the top or bottom of your monitor that changes based on your status. This is useful for roles like live streamers or telemedicine professionals who need constant confirmation that their systems are in the correct state. For more advanced setups, you can integrate these indicators with smart home systems (opens new window) to control physical lights in your room.
# Actionable Tips for Status Indicators:
- Establish a clear color code: Create a team standard that is intuitive and accessible. For example: red for muted/camera off, green for live microphone, and blue for a live camera. Use patterns or shapes alongside colors to support colorblind team members.
- Position for peripheral awareness: Place your indicator (physical or digital) just outside your primary line of sight so you can register its status without actively looking at it. The corner of a monitor or the top of a laptop screen works well.
- Use dual indicators for critical roles: For presenters or anyone in a client-facing role, use both a hardware light and a software overlay for redundancy and absolute certainty.
- Test in different lighting: Make sure your chosen indicator is clearly visible in your typical work environments, from a sunlit home office to a dimly lit conference room.
# 4. Create Role-Specific Control Profiles
Standardizing meeting controls is a good first step, but not all participants have the same needs. A sales professional’s most-used functions are different from those of an IT support agent or an event moderator. Creating role-specific control profiles tailors the user interface to the job function, placing the most important tools for that role front and center.
This approach builds on universal controls by creating optimized layouts for different use cases. It's an effective hybrid work best practice because it acknowledges that a one-size-fits-all solution is inefficient. A moderator needs instant access to mute-all and spotlight features, while a presenter needs one-touch screen sharing and recording controls.
# How to Implement Role-Specific Profiles
This is best achieved with programmable hardware like a Stream Deck or Loupedeck, which lets users switch between different button configurations with a single tap. An educator could have a "Teaching Mode" profile with buttons for starting breakout rooms, launching a poll, and managing participant hands. When they join a department meeting, they can switch to a "Participant Mode" with simpler mute, camera, and share functions.
Software-based macro tools can also achieve this by letting users load different sets of keyboard shortcuts or on-screen button layouts based on the active application or a chosen profile.
# Actionable Tips for Profile Creation:
- Survey your teams: Ask different departments (sales, support, HR) to list their top five most frequent actions during video calls. Use this data to build the baseline profiles.
- Create 3-5 core profiles: Start with common roles like 'Presenter', 'Moderator', and 'Participant'. Clearly label them for easy identification.
- Design quick-reference guides: For each profile, create a simple, laminated card showing the button layout and functions. This accelerates adoption.
- Test and iterate: Roll out the profiles to a small group of power users first. Gather feedback on the layout and make adjustments before a company-wide deployment.
# 5. Establish Meeting Pre-Flight Checklists
The first five minutes of a meeting are often wasted on technical troubleshooting: "Can you hear me now?", "Is my screen sharing?", "Sorry, my mic was muted." These minor delays disrupt momentum and look unprofessional, especially in high-stakes client calls or large webinars. A pre-flight checklist turns meeting preparation into a systematic, repeatable process, preventing these technical failures before they happen.
Implementing this simple verification procedure is a highly effective hybrid work best practice because it shifts troubleshooting from a reactive scramble to a proactive routine. It builds confidence and ensures that when the meeting starts, the focus is on the agenda, not the technology.
# How to Implement Pre-Flight Checklists
A pre-flight checklist can be a digital document, a physical card on your desk, or a calendar reminder with bullet points. Sales teams use them to run audio-video diagnostics before client demos, just as healthcare providers test telemedicine systems before patient appointments. The goal is to make the process quick and habitual.
This routine is valuable for external presentations or webinars where first impressions matter. By systematically checking your setup 5-10 minutes before every call, you minimize the chance of technical issues derailing your message. You can find a complete guide in our Pre-Meeting Success Playbook (opens new window).
By making this a standard operating procedure, you replace anxiety and uncertainty with a calm, controlled start to every virtual interaction.
# Actionable Tips for Your Checklist:
- Test Audio and Video: Join the meeting 2-3 minutes early. Check your microphone at a normal speaking volume and confirm your camera is positioned correctly with a clear background.
- Verify Lighting: Look at your video feed from the camera's perspective. Ensure your face is well-lit and free of harsh shadows or backlighting.
- Prepare Your Content: Have your presentation, documents, or browser tabs open and ready. Do a quick test to confirm screen sharing works with the intended monitor.
- Minimize Distractions: Mute all system notifications from email and messaging apps. Close any unnecessary, bandwidth-heavy applications to ensure a stable connection.
# 6. Develop Communication Norms for Hybrid Meeting Etiquette
Hybrid meetings often fail because of unwritten and conflicting expectations. In-office participants might chat before the call starts, leaving remote colleagues in silence. Remote attendees might keep their cameras off, making it hard for others to read their engagement. Establishing clear, explicit communication norms eliminates this ambiguity and prevents feelings of exclusion.
The goal is to create a shared rulebook for how your team interacts in meetings. This is a vital hybrid work best practice because it addresses the core challenge of hybrid work: creating an equitable experience for everyone, regardless of location. It ensures that meetings are productive, inclusive, and psychologically safe for all participants.
# How to Implement Hybrid Meeting Norms
Co-create the guidelines with your team rather than imposing them. Run a workshop or use a shared document where team members can contribute, discuss, and vote on norms related to camera usage, muting, interruptions, and chat. Differentiating norms by meeting type is also effective; a daily stand-up has different expectations than a formal quarterly review.
A global consulting firm might standardize a "mute by default, raise hand to speak" protocol for large client calls to manage cross-talk. Conversely, a small creative team might decide on a "camera optional, active chat participation expected" norm for brainstorming sessions to encourage ideas without video fatigue.
# Actionable Tips for Establishing Norms:
- Be explicit about video: Define when cameras are required (e.g., one-on-one check-ins) versus optional (e.g., large all-hands meetings). This removes anxiety and respects personal circumstances.
- Establish a "first-speaker" protocol: Address the issue of people talking over each other by implementing a hand-raise feature or a simple verbal cue system.
- Create a recording and access policy: Clearly state when meetings will be recorded and where they can be found. This supports asynchronous work and respects privacy by requiring consent.
- Document and review: Publish the agreed-upon norms in a central, easily accessible location. Schedule a review every six months to adjust the guidelines based on team feedback.
# 7. Optimize Network and Technical Infrastructure
A frozen screen during a presentation or choppy audio in a client negotiation can undermine credibility. These technical glitches are often the result of a weak network connection. Optimizing your technical infrastructure is not just an IT task; it is a basic requirement for professional communication in a distributed environment.
Ensuring every team member has reliable internet and quality hardware is a high-impact hybrid work best practice because it removes the primary source of meeting friction. This stability allows ideas, not technical issues, to be the focus of every interaction. A solid technical base gives everyone consistent, high-quality participation, regardless of their location.
# How to Implement a Resilient Infrastructure
This starts with investing in business-grade connectivity and hardware. Many companies now provide home office budgets that include broadband stipends or cover internet costs, acknowledging that home networks are now part of the corporate infrastructure. Sales teams often equip their reps with dual-monitor setups and noise-canceling headsets to create a professional remote environment. To support this model, it's necessary to think about the bigger picture of IT, as detailed in this guide on building secure scalable infrastructure for a distributed workforce (opens new window).
The goal is to create a baseline standard of technical performance for all employees. This prevents a two-tiered system where those with better home setups have an unfair advantage.
# Actionable Tips for Optimization:
- Prioritize a wired connection: Use an ethernet cable for your primary work computer, especially for important meetings or when screen sharing. It provides a more stable and faster connection than Wi-Fi.
- Test your bandwidth: Before a high-stakes call, run a quick check at a site like speedtest.net. You want to see at least 25 Mbps download and 10 Mbps upload for smooth HD video.
- Manage network traffic: Use your router's Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize traffic for your video conferencing applications (e.g., Zoom, Teams) over less critical activities like file downloads or streaming.
- Control software updates: Disable automatic software and OS updates during scheduled work hours. A background update can consume significant bandwidth and processing power, leading to poor call quality.
# 8. Implement Meeting Analytics and Behavior Tracking
Most teams treat meetings as a cost of doing business, rarely analyzing their effectiveness beyond gut feelings. Implementing meeting analytics means moving from assumption to data, collecting information on patterns, duration, and participation to reveal inefficiencies. This data-driven approach allows you to see what’s really happening in your meeting culture.
This strategy is an impactful hybrid work best practice because it quantifies problems that are otherwise invisible. It helps answer questions: Are our daily standups productive? Do our all-hands meetings engage remote staff? Why do certain project calls consistently run over schedule?
# How to Implement Meeting Analytics
Many video conferencing platforms, like Microsoft Teams and Zoom, offer built-in analytics that provide a starting point. These tools can generate reports showing average meeting length, participant numbers, and late joiners. Third-party tools can offer deeper insights, such as talk-time ratios, sentiment analysis, and keyword tracking to measure topic focus.
For instance, analytics might reveal that Tuesday morning meetings have the lowest engagement, prompting a shift in scheduling. Or data could show that meetings with more than seven people have a steep drop-off in participation, leading to a new guideline for smaller, more focused calls.
# Actionable Tips for Analytics:
- Be transparent about data collection: Clearly communicate to your team what data is being tracked and why. Frame it as a tool for collective improvement, not individual surveillance.
- Focus on aggregate trends: Analyze team-level or company-wide data. Look for patterns like the most common meeting start times, the average number of attendees, or which days have the most meeting overload.
- Share insights collaboratively: Present findings to teams and facilitate a discussion. Ask them for their interpretation and ideas for solutions. For example, "The data shows our team standups have very low talk time from half the participants. What can we change to make them more inclusive?"
- Track technical performance: Use analytics to identify which platforms or times of day result in the most technical glitches, helping IT make informed decisions about infrastructure and software.
# 9. Create Custom Integrations and Automation Workflows
Beyond controlling meetings, the next level of efficiency is making your meeting software work for you automatically. This involves building automated systems that react to meeting events like starting, ending, or recording. These triggers can then kick off actions in other applications, such as logging meeting notes, updating a CRM, or even adjusting your smart home lighting. This removes the manual busywork that surrounds meetings.
The idea is to connect your communication platform to the rest of your digital toolkit, creating a seamless flow of information. This is a powerful hybrid work best practice because it reduces administrative overhead and ensures follow-up actions aren't forgotten. It makes your workflow more resilient and less dependent on memory.
# How to Implement Workflow Automation
You can build these integrations using no-code platforms like Zapier or Make, which provide user-friendly interfaces for connecting thousands of apps. A sales professional can create an automation where ending a Zoom call automatically logs the meeting duration and participants in a Salesforce contact record. A customer support agent could have an automation that updates a support ticket with a link to the call recording as soon as the meeting concludes.
For more complex needs, developers can use direct API access to build custom solutions. The goal is to identify repetitive, rule-based tasks associated with your meetings and offload them to a machine.
# Actionable Tips for Automation:
- Start with simple triggers: Begin with a basic automation, such as posting a message to a Slack channel when a specific meeting starts or ends.
- Use existing platforms first: Leverage tools like Zapier, Make, or IFTTT before attempting to write custom code. They are faster to implement and easier to maintain.
- Document every workflow: Keep a simple log of what each automation does, what triggers it, and which systems it connects to. This is important for troubleshooting.
- Test in a safe environment: Before rolling out an automation that affects client data or team-wide systems, test it thoroughly with dummy accounts or in a staging environment.
# 10. Establish Meeting-Free Time Blocks and Focus Periods
The shift to hybrid work often leads to a calendar packed with back-to-back video calls, leaving little time for the actual work discussed in those meetings. Constant context-switching between collaboration and deep thought decimates productivity and leads to widespread meeting fatigue. Establishing protected focus time is a structural solution to this problem.
The idea is to embed uninterrupted work periods directly into the organizational schedule, shielding employees from a stream of meeting invites. This is a high-impact hybrid work best practice because it acknowledges that knowledge work requires sustained concentration, a resource that fragmented schedules destroy.
# How to Implement Focus Time
This policy can be implemented at the team, department, or company-wide level. For example, some organizations institute a "No Meeting Wednesday" or reserve specific afternoons for heads-down work. Google protects Wednesday afternoons as meeting-free for its engineers. Microsoft has piloted "no-meeting days" to combat digital overload. The key is to make it an official, respected part of the work culture.
This practice requires a cultural shift towards asynchronous communication. Instead of scheduling a meeting for a quick question, teams learn to rely on Slack, project management tools, or recorded video updates, preserving synchronous time for truly collaborative or urgent discussions.
# Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start with leadership: Executives and managers must model the behavior by blocking their own calendars and visibly respecting the focus periods of others.
- Use calendar automation: Leverage tools like Clockwise or settings in Google Calendar and Outlook to automatically schedule and defend focus time blocks for team members.
- Establish urgent-interruption protocols: Define what constitutes a true emergency that can override a focus block and specify the channel to use (e.g., a direct phone call, not a Slack message).
- Promote asynchronous alternatives: Actively train and encourage the use of tools like Loom for recorded updates or detailed project management comments to replace status meetings.
# Top 10 Hybrid Work Best Practices Comparison
| Approach | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource & Cost ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐ | Ideal Use Cases 📊 | Key Advantages & Tips 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardize Meeting Controls Across Platforms | Moderate — cross-platform mapping, testing, training | Low–Medium — configuration, documentation, minimal tooling | Greater consistency; fewer accidental unmute/camera errors; faster transitions | Cross-platform teams, sales, educators, frequent multi-platform users | Reduces cognitive load; document standards and test before key calls |
| Implement Physical Button Controls for Accessibility | Moderate — hardware setup, ergonomic placement, config | Medium–High — controllers, pedals, mounts, occasional replacements | Immediate tactile control, faster responses, better accessibility | Presenters, translators, webinar hosts, users with mobility/vision needs | Start with 5–7 core buttons; label clearly; position ergonomically |
| Enable Real-Time Visual Status Indicators | Low–Medium — integrate lights/widgets or hardware | Low–Medium — status lights or software widgets | Clear at-a-glance state; fewer embarrassing broadcasts; improved confidence | Remote presenters, educators, telemedicine, streaming | Use high-contrast colors; place in peripheral view; pair hardware+software for critical roles |
| Create Role-Specific Control Profiles | Moderate — role analysis and profile management | Low–Medium — software configuration, templates, training | Faster task access for each role; reduced clutter and errors | Moderators, presenters, support agents, translators, educators | Build 3–5 baseline profiles; enable quick-switch; name profiles clearly |
| Establish Meeting Pre-Flight Checklists | Low — create checklist and habit formation | Low — digital/print checklist; 5–10 minutes per meeting | Fewer technical failures; smoother high-stakes presentations | Webinars, sales demos, telemedicine, external presentations | Use a simple checklist; join early; verify mic, camera, lighting, and sharing |
| Develop Communication Norms for Hybrid Meeting Etiquette | Moderate — consensus-building and documentation | Low — time investment for policy and reinforcement | More inclusive meetings; reduced anxiety; better participation equity | Hybrid teams, global orgs, classrooms, distributed teams | Co-create norms with team; differentiate by meeting type; review periodically |
| Optimize Network and Technical Infrastructure | Medium–High — procurement, IT configuration, monitoring | High — bandwidth, hardware, UPS, ongoing service costs | Reliable meeting performance; improved AV quality; fewer interruptions | Sales, customer success, frequent presenters, remote-heavy teams | Prefer wired connections for critical calls; test bandwidth; provide stipends |
| Implement Meeting Analytics and Behavior Tracking | High — data pipelines, analytics, privacy controls | Medium–High — tooling, storage, compliance effort | Objective insights into meeting culture; identify inefficiencies | Large organizations studying meeting load and engagement | Be transparent; focus on systemic improvements; ensure legal compliance |
| Create Custom Integrations and Automation Workflows | High — development or integration-platform work | Medium–High — developer time or integration fees | Automated logging, improved workflow continuity, reduced manual work | Sales CRM integration, support ticket flows, smart office/home automation | Start simple with Zapier/Make; document automations; include manual overrides |
| Establish Meeting-Free Time Blocks and Focus Periods | Moderate — policy creation and cultural adoption | Low — calendar tools and leadership modeling | Increased deep work, reduced fatigue, better well‑being and productivity | Creative/technical roles, knowledge workers, remote-first orgs | Pilot voluntarily; model from leadership; use calendar automation and measure impact |
# Putting These Practices to Work
The shift to hybrid work is a fundamental change in how we collaborate. These ten practices offer a blueprint for navigating this new terrain with intention. They move beyond simple advice like "buy a good webcam" and into the systemic changes that address the core friction points of a distributed workforce. From standardizing meeting controls to establishing explicit communication norms, each practice is designed to replace ambiguity with clarity.
Adopting these hybrid work best practices isn't about imposing a rigid, top-down structure. It is about creating a predictable, equitable, and efficient environment where every team member can contribute effectively, regardless of their location. The goal is to make the technology and processes so seamless they become invisible, allowing focus to return to the work itself. This is where the real value lies: less time spent troubleshooting audio or battling meeting fatigue, and more time for creative problem-solving and meaningful collaboration.
# Your First Steps: From Idea to Implementation
Reading a list of best practices is one thing; integrating them is another. Start small and build momentum. Don't try to overhaul your entire hybrid model overnight.
- Conduct a Friction Audit: Ask your team: "What is the single most frustrating part of our hybrid meetings?" Is it the five minutes wasted while someone finds the mute button in a new app? Is it confusion over whether to use Slack, Teams, or email for a specific question? Pinpoint the most significant pain points first.
- Pick One or Two Practices: Based on your audit, select the practices that will deliver the most immediate impact. If meeting chaos is the issue, start with standardizing meeting controls and implementing a pre-flight checklist. If team culture feels disjointed, focus on communication norms and meeting-free time blocks.
- Pilot with a Small Group: Roll out your chosen practices with a single team or department. Use this pilot phase to gather feedback, identify unexpected challenges, and refine the process. This approach minimizes disruption and allows you to build a case study for wider adoption. You could equip your sales team with universal hardware controls and track the impact on their demo presentations before expanding the initiative.
- Codify and Communicate: Once you've refined a practice, formalize it. Update your company handbook, create a one-page guide, or record a short tutorial. Clear documentation turns an experiment into an official, shared habit. Announce the change and explain the "why" behind it, connecting it back to the friction points everyone identified.
# The Long-Term Impact of Deliberate Design
Mastering these hybrid work best practices yields benefits that extend far beyond smoother meetings. It cultivates a culture of inclusion where remote participants feel as present and empowered as their in-office colleagues. It enhances professional polish, ensuring that every client-facing interaction is seamless. Most importantly, it respects your team's most valuable asset: their time and attention. By removing the small, persistent technological and procedural hurdles, you free up cognitive resources for the complex, creative work that drives your business forward. This isn't just about managing a hybrid team; it's about unlocking its potential.
Ready to eliminate the most common source of meeting friction? MuteDeck provides the universal, physical controls discussed throughout these hybrid work best practices, giving you and your team a standardized way to manage any meeting on any platform. Take control of your hybrid work environment by visiting MuteDeck (opens new window) to see how it works.
